Introduction to Pulmonary Medicine
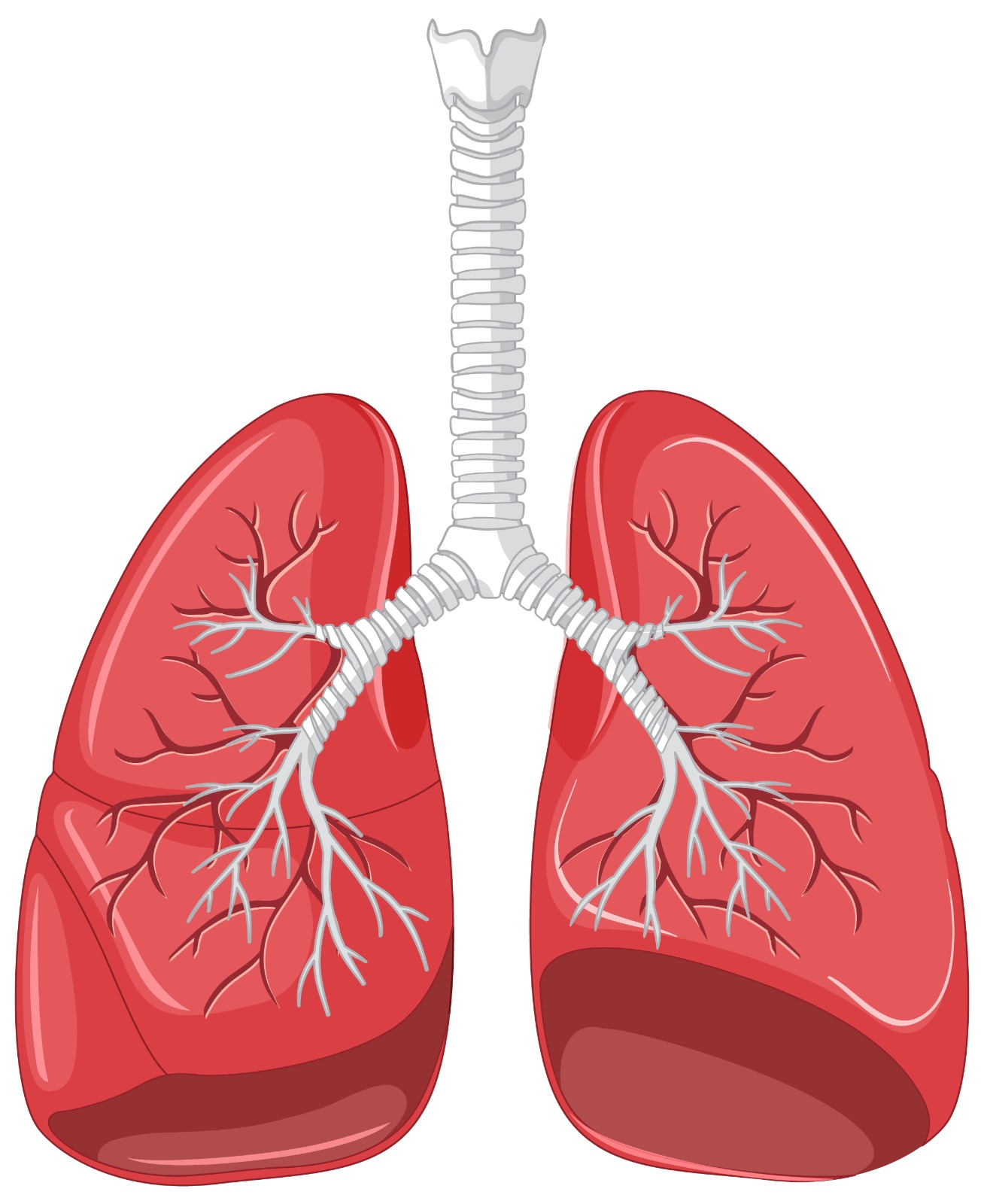
Pulmonary medicine, also known as pulmonology, is a specialized field of medicine focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases and disorders of the respiratory system. This includes the lungs, airways, and respiratory muscles. Pulmonologists, the physicians who specialize in this field, play a crucial role in addressing conditions that affect breathing and overall respiratory health.
Key Areas of Pulmonary Medicine
Asthma A chronic condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Pulmonologists manage asthma through medications, lifestyle changes, and monitoring.
● Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A group of lung diseases, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, that cause obstructed airflow and breathing difficulties. Treatment focuses on symptom relief, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life.
● Pulmonary FibrosisA condition where lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred, making it difficult for the lungs to work properly. Management includes medications, oxygen therapy, and in severe cases, lung transplantation.
● Lung CancerPulmonologists are involved in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning of lung cancer, often working alongside oncologists. Early detection and advanced treatments are crucial for improving survival rates
● Pulmonary HypertensionHigh blood pressure in the lungs' arteries, which can lead to heart failure if untreated. Treatment may involve medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes.
● Sleep ApneaA sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts. Pulmonologists often collaborate with sleep specialists to diagnose and treat sleep apnea using methods like CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) therapy
Diagnostic and Treatment Techniques
● Imaging TestsChest X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help visualize lung structures and identify abnormalities
● Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)These tests measure lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange to diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions
● BronchoscopyA procedure using a thin, flexible tube to examine the airways and collect samples for analysis.
● Biopsy
Taking a small sample of lung tissue to diagnose diseases such as cancer or infections.● MedicationsInhalers, bronchodilators, steroids, and other drugs to manage symptoms and treat underlying conditions.
● Oxygen TherapyProviding supplemental oxygen to patients with severe respiratory conditions.
● Pulmonary RehabilitationA comprehensive program that includes exercise, education, and support to improve respiratory health and quality of life
Importance of Pulmonary Medicine
Pulmonary medicine is vital for maintaining respiratory health and ensuring that individuals can breathe comfortably and effectively. Early detection and management of respiratory diseases can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Pulmonologists work in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, and research institutions, contributing to advancements in respiratory care and treatment.
Conclusion
Pulmonary medicine is a dynamic and essential field dedicated to addressing the complex and varied issues affecting the respiratory system. Through advanced diagnostic techniques, innovative treatments, and ongoing research, pulmonologists help patients achieve better respiratory health and enhance their overall well-being